Ebola, a severe and often deadly viral illness, has been a major public health concern in recent years. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has been at the forefront of efforts to combat the disease, providing critical information and resources to help prevent and control outbreaks. In this article, we will delve into the basics of Ebola, its symptoms, transmission, and prevention, as well as the CDC's role in fighting the disease.
What is Ebola?
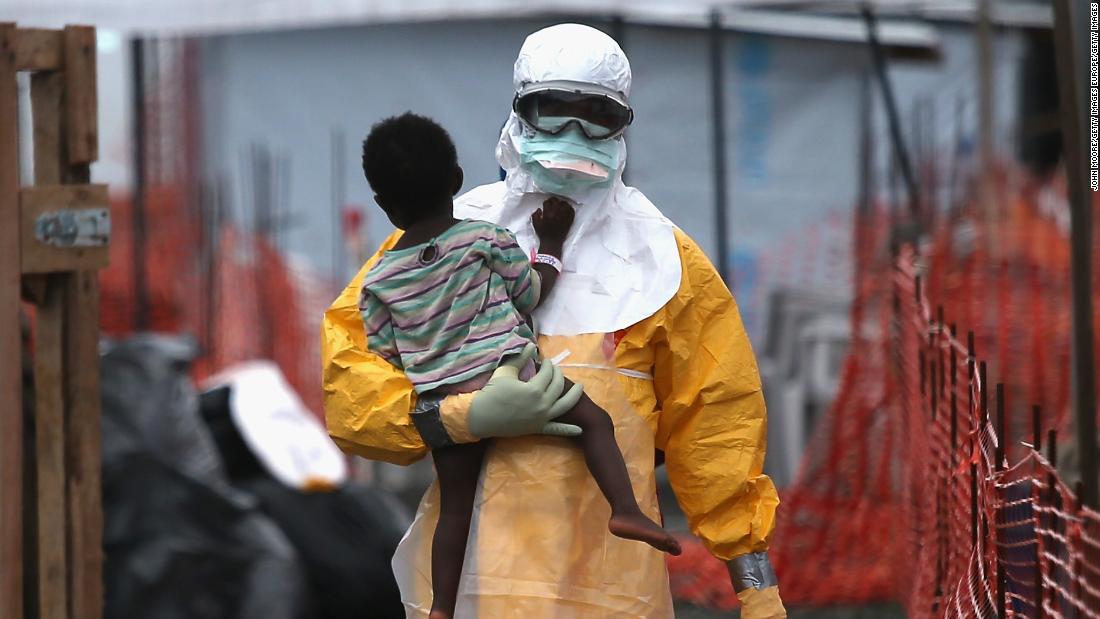
Ebola is a viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Ebola virus. It is a severe and often fatal illness that affects humans and animals, with a mortality rate of up to 90% if left untreated. The virus is named after the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where it was first identified in 1976. Since then, there have been several outbreaks of the disease in Africa, with the most recent and largest outbreak occurring in West Africa from 2014 to 2016.
Symptoms of Ebola
The symptoms of Ebola can vary, but they often include:
Fever
Headache
Muscle pain
Weakness
Fatigue
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Abdominal pain
Bleeding or bruising
These symptoms can appear anywhere from 2 to 21 days after exposure to the virus, with most people showing symptoms within 8-10 days.
How is Ebola Transmitted?
Ebola is transmitted through:
Direct contact with infected blood, bodily fluids, or tissues
Contact with objects contaminated with infected bodily fluids
Close contact with an infected person, such as touching or caring for them
Contact with infected animals, such as fruit bats or nonhuman primates
The virus can also be spread through medical procedures, such as injections or surgeries, if proper infection control measures are not in place.
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling Ebola requires a multi-faceted approach. The CDC recommends:
Avoiding close contact with people who are sick with Ebola
Avoiding contact with infected bodily fluids
Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and masks, when caring for patients
Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing
Avoiding eating or handling bushmeat, which can carry the virus
The CDC also provides guidance on infection control and prevention in healthcare settings, including the use of PPE, proper disinfection and sterilization, and safe handling of medical waste.
CDC's Role in Fighting Ebola
The CDC plays a critical role in preventing and controlling Ebola outbreaks. The agency:
Provides technical assistance and support to affected countries
Conducts research on the virus and its transmission
Develops and distributes educational materials and guidance on prevention and control
Supports the development of vaccines and treatments
Deploys personnel to affected areas to assist with outbreak response and control
In conclusion, Ebola is a serious and often deadly disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention and control. The CDC is a trusted source of information and guidance on Ebola, and their efforts have been instrumental in preventing and controlling outbreaks. By understanding the basics of Ebola and taking steps to prevent its transmission, we can work together to reduce the risk of this devastating disease.
Source: CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended to provide medical advice. If you have concerns about Ebola or any other health issue, please consult a qualified healthcare professional.